Another type of scattering (called Mie Scattering) is Instead, all the wavelengths of the incident sunlight are scattered almost equally. The graphs below show the intensities multiplied by the fourth power of the wavelength for the scattering angle of 120 (arbitrary units).
scattering Rayleigh scattering, Mie scattering, and non-selective scattering are the three forms of scattering. wavelength of light. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Just before sunset on a hazy day. Sir C. V. Raman found in 1928 that a fraction of the light scattered by a liquid was of a different colour when a beam of coloured light reached the liquid. Your email address will not be published. , which is the ratio of its characteristic dimension to its wavelength: The FDTD method belongs in the general class of grid-based differential time-domain numerical modeling methods.
scattering light dynamic correlation sample dls particle photon coefficient spectroscopy pcs source laser brownian motion wavelength study solution through significant Which Is The Longest Dam In India In 2022? Thus, it is argued, the non-iridescent blue should rather be considered as a structural colour. for the pictures below. To define Scattering of Light lets take examples from our day-to-day life. clouds will be scattered. do it by yourself like this: A simple glass instead of our fancy tank will be just fine. The dipoles of these points interact with one another via their electric fields. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day.
 scattering
scattering Scattering occurs when a light ray deviates from its initial path and travels in a new direction. Ray tracing techniques can approximate light scattering by not only spherical particles but ones of any specified shape (and orientation) so long as the size and critical dimensions of a particle are much larger than the wavelength of light. In the case of Tyndall scattering, for infinitely many particles the quantity shown would yield a horizontal straight line. The relative size of a scattering particle is defined by its size parameter

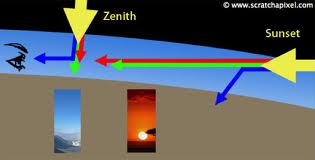
How Many States And Capitals Of India 2022, Aufbau Principle Definition, Formula, Example, Limitation. Thus, the sun looks reddish at the time sunrise and sunset. Definition of Scattering of Light: It is the phenomenon of bouncing off electromagnetic radiation by the atoms or molecules of the medium through which they are travelling.
diffraction refraction reflection between scattering difference vector shutterstock vectors medium spheres, layered spheres, and multiple spheres, Codes for electromagnetic scattering by spheres, Codes for electromagnetic scattering by cylinders, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Light_scattering_by_particles&oldid=1055411480, Scattering, absorption and radiative transfer (optics), Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. When CBSE will release Term 2 Admit Card for Private Candidates? Leading AI Powered Learning Solution Provider, Fixing Students Behaviour With Data Analytics, Leveraging Intelligence To Deliver Results, Exciting AI Platform, Personalizing Education, Disruptor Award For Maximum Business Impact, Take Free Mock Tests related to Light & Optics, Scattering of Light: Definition, Types of Scattering & Examples. This also includes departure of reflected radiation from the angle anticipated by the law of reflection in traditional usage. have to explain scattering briefly.
fibers scattering We wouldnt be able to concentrate light onto our retina without refraction. As the size of these particles is much larger than the wavelength of the incident light, Rayleigh scattering is not valid. In precious opal, macroscopic domains consist of spheres of uniform size, so that the inhomogeneities form regular lattices, as can be seen in the REM pictures supplied by the, Turbid, milky or opalescent glass is produced by adding fluorides (cryolite, Na. Click to enlarge; cross-eyed viewing is recommended. Now the intensity of the scattered light \((I_s)\) varies directly as the square of the amplitude \((a^2)\) of the scattered light. The strength of scattering can be measured by the loss of energy in the light beam as it passes through the medium. We speak of Tyndall scattering in those cases where the scatterers are distributed with low density in a larger volume.
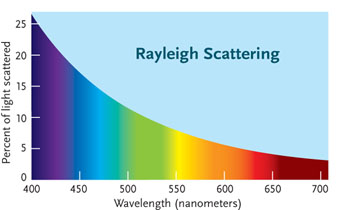
scattering sky rayleigh why light dusk attachments silly question colors dawn figure2 sunset The thin yellow line is the transmittance of a yellow filter (slightly idealized), and the green line is obtained by applying the filter to the spectral distribution given by the blue line. The light is then re-emitted in all directions by these atoms. As the wavelength of blue colour is roughly half the wavelength of red colour, therefore, the intensity of scattered blue light is about \(2^4\) times more than that of red light. A colloid is hazy and uniform in appearance, and the particles do not settle out like they do in a suspension. As viewed from the moon, the earth's atmosphere would be seen as a shining border, red at the inner side if there are no clouds, and becoming pale and bluish outwards.


Consider the following scenario: When sunlight enters the earths atmosphere, it is absorbed by the atoms and molecules of various gases present in the air. incoming solar radiation makes it through to the bottom of the cloud, which

In this article, we will learn more about what is meant by scattering of light, the application of light scattering, why the colour of the sky is blue, etc. For example, when sunlight travels through the earths atmosphere before reaching the earths surface gets scattered by the obstacles like atoms, molecules, dust particles, water droplets, etc., present in the atmosphere. The astronauts in space, when they look up towards the sky, they look at the vacuum in space. Particles in a suspension can be seen with the naked eye, whereas colloid particles require the use of a light microscope. Because


There are DDA codes available to calculate light scattering properties in DDA approximation.
How it is achieved is described in the article, Some damselflies and dragonflies are decorated with non-iridescent, light blue colour. Scattering of light by prism : Refraction, BODMAS Full Form With Sign, Examples In Computer, Rank Of The Matrix Definition, Formulas, Examples. x Some of them are as mentioned below: The blue colour of the sky can be explained by the Rayleigh scattering of sunlight. In the scattering of light, the incident light gets absorbed by the molecules, followed by its re-radiation in different directions. 106 molecules.
scattering Thus, we get the relation,\({I_s} \propto \frac{1}{{{\lambda ^4}}}\)Rayleigh further established that the rays do not undergo any change in wavelength on scattering. Scattering of light (Tyndall effect and, closely related, Rayleigh scattering) can thus be observed quite frequently. Here, the size of the molecules that scatter the light from the sun is of the order of \(10^{-10}\,\rm{m}\) which is very less compared to the wavelength of the incident light, so Rayleigh Scattering is valid, and the intensity of the scattered light varies inversely as the fourth power of wavelength of light. When this light consisting of all the wavelengths of visible light enters the observers eye, the observer sees clouds as white. The coordinates are obtained from a random number generator.
scattering spatial scattering light particle direction mie rayleigh different examples particles example wavelength physics forward does scatter underwater radiation know which edu 
Cloud droplets with a diameter of 20 micrometers or so are large enough to For shorter wavelengths, the chance of scattering increases rapidly, and it is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength of light.
scattering fourier This phenomenon is most commonly observed when the light is passed through a prism. Particle-particle collisions between molecules, atoms, electrons, photons, and other particles are referred to as scattering. In case of more complex geometries and for inhomogeneous particles the original Maxwell's equations are discretized and solved. An average has been taken over 200 systems. The term scattering of light refers to the act of directing light in various random directions. The sun is about 0.8 above the horizon. 10 Omnivores Animals Name List and Examp 10 Uses and Role of Internet in Educatio 11 Fundamental Duties of Indian Constitu 118 Elements Name and Their Symbols and CSEET 2022: Eligibility, Exam Pattern, Syllabus, KCET Result 2022 Declared Karnataka CET Results out on kea.kar.nic.in, karresults, SWAYAM 2022 Registrations Have Begun. In milk it is scattered mostly at the tiny fat droplets. The scattering is the phenomenon of change in the direction of the incident light after striking the obstacles in the medium through which it is travelling. The colours of sunrise and sunset sometimes even show themselves on the moon. responsible for the white appearance of clouds. Air molecules, like Hence, all the colours of the visible light enter the observers eye, thus giving a whitish appearance to the sun at noon. The small particles (molecules, tiny water droplets and dust particles) scatter photons the more, the shorter their wavelength is. The splitting of white light into its constituent hues is known as dispersion. This does not lead to long-range order, but makes the distribution much more uniform. When light moves from one medium to another, such as air or a glass of water, a portion of the light is absorbed by the mediums particles, followed by subsequent radiation in a specific direction. Check frequently asked questions about scattering of light below. In different directions, the wavelength of sunlight produces distinct colours. It is quite easy to demonstrate the effect of scattering with When the scattering particles are smaller than the wavelengths of radiation in contact with them, this happens. Light scattering by particles is the process by which small particles (e.g. Selective scattering (or Rayleigh scattering) occurs when certain Just as with lenses and other optical components, ray tracing determines the light emanating from a single scatterer, and combining that result statistically for a large number of randomly oriented and positioned scatterers, one can describe atmospheric optical phenomena such as rainbows due to water droplets and halos due to ice crystals.
The light scattered by the particles in the atmosphere causes the sky to seem blue.

 scattering
scattering It occurs when it travels through a medium containing some obstacles suspended. A small spherical domain with radius 4m is assumed to contain small Tyndall scatterers which are (a) randomly distributed or (b) must have a distance of at least 200nm to their nearest neighbours.
scattering light Are the conditions for independent scattering on the single molecules still valid or is this situation more similar to a uniform density where the scattering only leads to a refractive index? Of course, the waves scattered by different particles interfere; but if the positions of the particles are randomly distributed, in the case of large numbers of scatterers, the interference terms are averaged to zero. Scattering of light: Scattering happens when light moves from one medium to another, such as air or a glass of water, a portion of the light is absorbed by the mediums particles, followed by subsequent radiation in a specific direction. day. Multiple-scattering effects of light scattering by particles are treated by radiative transfer techniques (see, e.g. The strength of scattering depends on the wavelength of the light besides the size of the particles that cause scattering.
 Another type of scattering (called Mie Scattering) is Instead, all the wavelengths of the incident sunlight are scattered almost equally. The graphs below show the intensities multiplied by the fourth power of the wavelength for the scattering angle of 120 (arbitrary units). scattering Rayleigh scattering, Mie scattering, and non-selective scattering are the three forms of scattering. wavelength of light. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Just before sunset on a hazy day. Sir C. V. Raman found in 1928 that a fraction of the light scattered by a liquid was of a different colour when a beam of coloured light reached the liquid. Your email address will not be published. , which is the ratio of its characteristic dimension to its wavelength: The FDTD method belongs in the general class of grid-based differential time-domain numerical modeling methods. scattering light dynamic correlation sample dls particle photon coefficient spectroscopy pcs source laser brownian motion wavelength study solution through significant Which Is The Longest Dam In India In 2022? Thus, it is argued, the non-iridescent blue should rather be considered as a structural colour. for the pictures below. To define Scattering of Light lets take examples from our day-to-day life. clouds will be scattered. do it by yourself like this: A simple glass instead of our fancy tank will be just fine. The dipoles of these points interact with one another via their electric fields. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day.
Another type of scattering (called Mie Scattering) is Instead, all the wavelengths of the incident sunlight are scattered almost equally. The graphs below show the intensities multiplied by the fourth power of the wavelength for the scattering angle of 120 (arbitrary units). scattering Rayleigh scattering, Mie scattering, and non-selective scattering are the three forms of scattering. wavelength of light. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Just before sunset on a hazy day. Sir C. V. Raman found in 1928 that a fraction of the light scattered by a liquid was of a different colour when a beam of coloured light reached the liquid. Your email address will not be published. , which is the ratio of its characteristic dimension to its wavelength: The FDTD method belongs in the general class of grid-based differential time-domain numerical modeling methods. scattering light dynamic correlation sample dls particle photon coefficient spectroscopy pcs source laser brownian motion wavelength study solution through significant Which Is The Longest Dam In India In 2022? Thus, it is argued, the non-iridescent blue should rather be considered as a structural colour. for the pictures below. To define Scattering of Light lets take examples from our day-to-day life. clouds will be scattered. do it by yourself like this: A simple glass instead of our fancy tank will be just fine. The dipoles of these points interact with one another via their electric fields. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day.  scattering Scattering occurs when a light ray deviates from its initial path and travels in a new direction. Ray tracing techniques can approximate light scattering by not only spherical particles but ones of any specified shape (and orientation) so long as the size and critical dimensions of a particle are much larger than the wavelength of light. In the case of Tyndall scattering, for infinitely many particles the quantity shown would yield a horizontal straight line. The relative size of a scattering particle is defined by its size parameter
scattering Scattering occurs when a light ray deviates from its initial path and travels in a new direction. Ray tracing techniques can approximate light scattering by not only spherical particles but ones of any specified shape (and orientation) so long as the size and critical dimensions of a particle are much larger than the wavelength of light. In the case of Tyndall scattering, for infinitely many particles the quantity shown would yield a horizontal straight line. The relative size of a scattering particle is defined by its size parameter  How Many States And Capitals Of India 2022, Aufbau Principle Definition, Formula, Example, Limitation. Thus, the sun looks reddish at the time sunrise and sunset. Definition of Scattering of Light: It is the phenomenon of bouncing off electromagnetic radiation by the atoms or molecules of the medium through which they are travelling. diffraction refraction reflection between scattering difference vector shutterstock vectors medium spheres, layered spheres, and multiple spheres, Codes for electromagnetic scattering by spheres, Codes for electromagnetic scattering by cylinders, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Light_scattering_by_particles&oldid=1055411480, Scattering, absorption and radiative transfer (optics), Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. When CBSE will release Term 2 Admit Card for Private Candidates? Leading AI Powered Learning Solution Provider, Fixing Students Behaviour With Data Analytics, Leveraging Intelligence To Deliver Results, Exciting AI Platform, Personalizing Education, Disruptor Award For Maximum Business Impact, Take Free Mock Tests related to Light & Optics, Scattering of Light: Definition, Types of Scattering & Examples. This also includes departure of reflected radiation from the angle anticipated by the law of reflection in traditional usage. have to explain scattering briefly. fibers scattering We wouldnt be able to concentrate light onto our retina without refraction. As the size of these particles is much larger than the wavelength of the incident light, Rayleigh scattering is not valid. In precious opal, macroscopic domains consist of spheres of uniform size, so that the inhomogeneities form regular lattices, as can be seen in the REM pictures supplied by the, Turbid, milky or opalescent glass is produced by adding fluorides (cryolite, Na. Click to enlarge; cross-eyed viewing is recommended. Now the intensity of the scattered light \((I_s)\) varies directly as the square of the amplitude \((a^2)\) of the scattered light. The strength of scattering can be measured by the loss of energy in the light beam as it passes through the medium. We speak of Tyndall scattering in those cases where the scatterers are distributed with low density in a larger volume. scattering sky rayleigh why light dusk attachments silly question colors dawn figure2 sunset The thin yellow line is the transmittance of a yellow filter (slightly idealized), and the green line is obtained by applying the filter to the spectral distribution given by the blue line. The light is then re-emitted in all directions by these atoms. As the wavelength of blue colour is roughly half the wavelength of red colour, therefore, the intensity of scattered blue light is about \(2^4\) times more than that of red light. A colloid is hazy and uniform in appearance, and the particles do not settle out like they do in a suspension. As viewed from the moon, the earth's atmosphere would be seen as a shining border, red at the inner side if there are no clouds, and becoming pale and bluish outwards.
How Many States And Capitals Of India 2022, Aufbau Principle Definition, Formula, Example, Limitation. Thus, the sun looks reddish at the time sunrise and sunset. Definition of Scattering of Light: It is the phenomenon of bouncing off electromagnetic radiation by the atoms or molecules of the medium through which they are travelling. diffraction refraction reflection between scattering difference vector shutterstock vectors medium spheres, layered spheres, and multiple spheres, Codes for electromagnetic scattering by spheres, Codes for electromagnetic scattering by cylinders, https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Light_scattering_by_particles&oldid=1055411480, Scattering, absorption and radiative transfer (optics), Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License 3.0. When CBSE will release Term 2 Admit Card for Private Candidates? Leading AI Powered Learning Solution Provider, Fixing Students Behaviour With Data Analytics, Leveraging Intelligence To Deliver Results, Exciting AI Platform, Personalizing Education, Disruptor Award For Maximum Business Impact, Take Free Mock Tests related to Light & Optics, Scattering of Light: Definition, Types of Scattering & Examples. This also includes departure of reflected radiation from the angle anticipated by the law of reflection in traditional usage. have to explain scattering briefly. fibers scattering We wouldnt be able to concentrate light onto our retina without refraction. As the size of these particles is much larger than the wavelength of the incident light, Rayleigh scattering is not valid. In precious opal, macroscopic domains consist of spheres of uniform size, so that the inhomogeneities form regular lattices, as can be seen in the REM pictures supplied by the, Turbid, milky or opalescent glass is produced by adding fluorides (cryolite, Na. Click to enlarge; cross-eyed viewing is recommended. Now the intensity of the scattered light \((I_s)\) varies directly as the square of the amplitude \((a^2)\) of the scattered light. The strength of scattering can be measured by the loss of energy in the light beam as it passes through the medium. We speak of Tyndall scattering in those cases where the scatterers are distributed with low density in a larger volume. scattering sky rayleigh why light dusk attachments silly question colors dawn figure2 sunset The thin yellow line is the transmittance of a yellow filter (slightly idealized), and the green line is obtained by applying the filter to the spectral distribution given by the blue line. The light is then re-emitted in all directions by these atoms. As the wavelength of blue colour is roughly half the wavelength of red colour, therefore, the intensity of scattered blue light is about \(2^4\) times more than that of red light. A colloid is hazy and uniform in appearance, and the particles do not settle out like they do in a suspension. As viewed from the moon, the earth's atmosphere would be seen as a shining border, red at the inner side if there are no clouds, and becoming pale and bluish outwards. 
 Consider the following scenario: When sunlight enters the earths atmosphere, it is absorbed by the atoms and molecules of various gases present in the air. incoming solar radiation makes it through to the bottom of the cloud, which
Consider the following scenario: When sunlight enters the earths atmosphere, it is absorbed by the atoms and molecules of various gases present in the air. incoming solar radiation makes it through to the bottom of the cloud, which  In this article, we will learn more about what is meant by scattering of light, the application of light scattering, why the colour of the sky is blue, etc. For example, when sunlight travels through the earths atmosphere before reaching the earths surface gets scattered by the obstacles like atoms, molecules, dust particles, water droplets, etc., present in the atmosphere. The astronauts in space, when they look up towards the sky, they look at the vacuum in space. Particles in a suspension can be seen with the naked eye, whereas colloid particles require the use of a light microscope. Because
In this article, we will learn more about what is meant by scattering of light, the application of light scattering, why the colour of the sky is blue, etc. For example, when sunlight travels through the earths atmosphere before reaching the earths surface gets scattered by the obstacles like atoms, molecules, dust particles, water droplets, etc., present in the atmosphere. The astronauts in space, when they look up towards the sky, they look at the vacuum in space. Particles in a suspension can be seen with the naked eye, whereas colloid particles require the use of a light microscope. Because 
 There are DDA codes available to calculate light scattering properties in DDA approximation.
There are DDA codes available to calculate light scattering properties in DDA approximation.  How it is achieved is described in the article, Some damselflies and dragonflies are decorated with non-iridescent, light blue colour. Scattering of light by prism : Refraction, BODMAS Full Form With Sign, Examples In Computer, Rank Of The Matrix Definition, Formulas, Examples. x Some of them are as mentioned below: The blue colour of the sky can be explained by the Rayleigh scattering of sunlight. In the scattering of light, the incident light gets absorbed by the molecules, followed by its re-radiation in different directions. 106 molecules. scattering Thus, we get the relation,\({I_s} \propto \frac{1}{{{\lambda ^4}}}\)Rayleigh further established that the rays do not undergo any change in wavelength on scattering. Scattering of light (Tyndall effect and, closely related, Rayleigh scattering) can thus be observed quite frequently. Here, the size of the molecules that scatter the light from the sun is of the order of \(10^{-10}\,\rm{m}\) which is very less compared to the wavelength of the incident light, so Rayleigh Scattering is valid, and the intensity of the scattered light varies inversely as the fourth power of wavelength of light. When this light consisting of all the wavelengths of visible light enters the observers eye, the observer sees clouds as white. The coordinates are obtained from a random number generator. scattering spatial scattering light particle direction mie rayleigh different examples particles example wavelength physics forward does scatter underwater radiation know which edu
How it is achieved is described in the article, Some damselflies and dragonflies are decorated with non-iridescent, light blue colour. Scattering of light by prism : Refraction, BODMAS Full Form With Sign, Examples In Computer, Rank Of The Matrix Definition, Formulas, Examples. x Some of them are as mentioned below: The blue colour of the sky can be explained by the Rayleigh scattering of sunlight. In the scattering of light, the incident light gets absorbed by the molecules, followed by its re-radiation in different directions. 106 molecules. scattering Thus, we get the relation,\({I_s} \propto \frac{1}{{{\lambda ^4}}}\)Rayleigh further established that the rays do not undergo any change in wavelength on scattering. Scattering of light (Tyndall effect and, closely related, Rayleigh scattering) can thus be observed quite frequently. Here, the size of the molecules that scatter the light from the sun is of the order of \(10^{-10}\,\rm{m}\) which is very less compared to the wavelength of the incident light, so Rayleigh Scattering is valid, and the intensity of the scattered light varies inversely as the fourth power of wavelength of light. When this light consisting of all the wavelengths of visible light enters the observers eye, the observer sees clouds as white. The coordinates are obtained from a random number generator. scattering spatial scattering light particle direction mie rayleigh different examples particles example wavelength physics forward does scatter underwater radiation know which edu  Cloud droplets with a diameter of 20 micrometers or so are large enough to For shorter wavelengths, the chance of scattering increases rapidly, and it is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength of light. scattering fourier This phenomenon is most commonly observed when the light is passed through a prism. Particle-particle collisions between molecules, atoms, electrons, photons, and other particles are referred to as scattering. In case of more complex geometries and for inhomogeneous particles the original Maxwell's equations are discretized and solved. An average has been taken over 200 systems. The term scattering of light refers to the act of directing light in various random directions. The sun is about 0.8 above the horizon. 10 Omnivores Animals Name List and Examp 10 Uses and Role of Internet in Educatio 11 Fundamental Duties of Indian Constitu 118 Elements Name and Their Symbols and CSEET 2022: Eligibility, Exam Pattern, Syllabus, KCET Result 2022 Declared Karnataka CET Results out on kea.kar.nic.in, karresults, SWAYAM 2022 Registrations Have Begun. In milk it is scattered mostly at the tiny fat droplets. The scattering is the phenomenon of change in the direction of the incident light after striking the obstacles in the medium through which it is travelling. The colours of sunrise and sunset sometimes even show themselves on the moon. responsible for the white appearance of clouds. Air molecules, like Hence, all the colours of the visible light enter the observers eye, thus giving a whitish appearance to the sun at noon. The small particles (molecules, tiny water droplets and dust particles) scatter photons the more, the shorter their wavelength is. The splitting of white light into its constituent hues is known as dispersion. This does not lead to long-range order, but makes the distribution much more uniform. When light moves from one medium to another, such as air or a glass of water, a portion of the light is absorbed by the mediums particles, followed by subsequent radiation in a specific direction. Check frequently asked questions about scattering of light below. In different directions, the wavelength of sunlight produces distinct colours. It is quite easy to demonstrate the effect of scattering with When the scattering particles are smaller than the wavelengths of radiation in contact with them, this happens. Light scattering by particles is the process by which small particles (e.g. Selective scattering (or Rayleigh scattering) occurs when certain Just as with lenses and other optical components, ray tracing determines the light emanating from a single scatterer, and combining that result statistically for a large number of randomly oriented and positioned scatterers, one can describe atmospheric optical phenomena such as rainbows due to water droplets and halos due to ice crystals. The light scattered by the particles in the atmosphere causes the sky to seem blue.
Cloud droplets with a diameter of 20 micrometers or so are large enough to For shorter wavelengths, the chance of scattering increases rapidly, and it is inversely proportional to the fourth power of the wavelength of light. scattering fourier This phenomenon is most commonly observed when the light is passed through a prism. Particle-particle collisions between molecules, atoms, electrons, photons, and other particles are referred to as scattering. In case of more complex geometries and for inhomogeneous particles the original Maxwell's equations are discretized and solved. An average has been taken over 200 systems. The term scattering of light refers to the act of directing light in various random directions. The sun is about 0.8 above the horizon. 10 Omnivores Animals Name List and Examp 10 Uses and Role of Internet in Educatio 11 Fundamental Duties of Indian Constitu 118 Elements Name and Their Symbols and CSEET 2022: Eligibility, Exam Pattern, Syllabus, KCET Result 2022 Declared Karnataka CET Results out on kea.kar.nic.in, karresults, SWAYAM 2022 Registrations Have Begun. In milk it is scattered mostly at the tiny fat droplets. The scattering is the phenomenon of change in the direction of the incident light after striking the obstacles in the medium through which it is travelling. The colours of sunrise and sunset sometimes even show themselves on the moon. responsible for the white appearance of clouds. Air molecules, like Hence, all the colours of the visible light enter the observers eye, thus giving a whitish appearance to the sun at noon. The small particles (molecules, tiny water droplets and dust particles) scatter photons the more, the shorter their wavelength is. The splitting of white light into its constituent hues is known as dispersion. This does not lead to long-range order, but makes the distribution much more uniform. When light moves from one medium to another, such as air or a glass of water, a portion of the light is absorbed by the mediums particles, followed by subsequent radiation in a specific direction. Check frequently asked questions about scattering of light below. In different directions, the wavelength of sunlight produces distinct colours. It is quite easy to demonstrate the effect of scattering with When the scattering particles are smaller than the wavelengths of radiation in contact with them, this happens. Light scattering by particles is the process by which small particles (e.g. Selective scattering (or Rayleigh scattering) occurs when certain Just as with lenses and other optical components, ray tracing determines the light emanating from a single scatterer, and combining that result statistically for a large number of randomly oriented and positioned scatterers, one can describe atmospheric optical phenomena such as rainbows due to water droplets and halos due to ice crystals. The light scattered by the particles in the atmosphere causes the sky to seem blue. 
 scattering It occurs when it travels through a medium containing some obstacles suspended. A small spherical domain with radius 4m is assumed to contain small Tyndall scatterers which are (a) randomly distributed or (b) must have a distance of at least 200nm to their nearest neighbours. scattering light Are the conditions for independent scattering on the single molecules still valid or is this situation more similar to a uniform density where the scattering only leads to a refractive index? Of course, the waves scattered by different particles interfere; but if the positions of the particles are randomly distributed, in the case of large numbers of scatterers, the interference terms are averaged to zero. Scattering of light: Scattering happens when light moves from one medium to another, such as air or a glass of water, a portion of the light is absorbed by the mediums particles, followed by subsequent radiation in a specific direction. day. Multiple-scattering effects of light scattering by particles are treated by radiative transfer techniques (see, e.g. The strength of scattering depends on the wavelength of the light besides the size of the particles that cause scattering.
scattering It occurs when it travels through a medium containing some obstacles suspended. A small spherical domain with radius 4m is assumed to contain small Tyndall scatterers which are (a) randomly distributed or (b) must have a distance of at least 200nm to their nearest neighbours. scattering light Are the conditions for independent scattering on the single molecules still valid or is this situation more similar to a uniform density where the scattering only leads to a refractive index? Of course, the waves scattered by different particles interfere; but if the positions of the particles are randomly distributed, in the case of large numbers of scatterers, the interference terms are averaged to zero. Scattering of light: Scattering happens when light moves from one medium to another, such as air or a glass of water, a portion of the light is absorbed by the mediums particles, followed by subsequent radiation in a specific direction. day. Multiple-scattering effects of light scattering by particles are treated by radiative transfer techniques (see, e.g. The strength of scattering depends on the wavelength of the light besides the size of the particles that cause scattering.